Spring Boot Interview Questions
In this article, we have presented 50 Interview questions on Spring Boot covering several topics including 20 Multiple choice questions (MCQs) and 30 Descriptive questions with answers.
Table of contents:
General Spring Boot questions
1. What is the Spring Boot and why is it popular?
Spring Boot is a Java framework for developing stand-alone Spring applications that can be started with minimal configuration setups. It takes care of Spring dependency management, introduces opinionated autoconfiguration, and simplifies deployment.
Spring Boot is one of the most popular frameworks among Java developers because it utilizes advantages of other Spring projects like Spring Core, Spring MVC, Spring Security, and Spring Cloud and brings its features on top of it:
- Fast to get started and accessible in different development environments
- Opinionated by design but with the full support of customization
- Provides embedded servers (Tomcat by default, Jetty, or Undertow), out-of-the-box security, metrics, and application health features
- Supports the optional use of the command-line interface
- Has lots of free guides, tutorials, docs, and textbooks to learn from
2. What are the disadvantages of the Spring Boot?
There are fewer Spring Boot disadvantages than advantages, but arguably the list of disadvantages may include:
- Lack of control over the code with Spring Boot automatic dependency management and autoconfiguration
- Spring Boot is more oriented towards microservices architecture than monolithic apps
- Although starting up with Spring Boot is easy, developing advanced stuff requires a good understanding of underlying Spring Boot and Spring mechanics
3. Compare Spring and Spring Boot
The Spring can be thought of as the comprehensive programming and configuration model for Java-based applications, which includes tools for developing, testing, and integration:
- Core: dependency injection, events, type conversion, data binding, AOP
- Data Access: JDBC, ORM, transactions, DAO support
- Web: MVC and WebFlux frameworks
- Tests: Spring MVC Test, mock objects, TestContext framework
- Security: Spring Security module
- Languages: Java, Kotlin, Groovy
The Spring Boot builds on top of the Spring technologies and simplifies development and Spring-related configurations allowing to program reactively with a focus on business logic. New features of the Spring Boot over the Spring include:
- Starter dependencies
- Auto-configuration
- Embedded servers
- In-memory database (H2, HSQLDB, or Derby)
- Configurable actuators
Setting up a project with Spring Boot
4. What are the ways to create a Spring Boot project?
The easiest way to start developing with Spring Boot is the Spring Initializr,
other options include Spring plug-ins for IDE, Spring Boot CLI commands, or manual creation. With manual creation though it is important to follow the correct project structure so Spring Boot does not miss components during the scan.
5. How does Initialzr help with dependency management?
Spring Initializr is a web application that generates a skeleton structure and building file for the Spring Boot project. It allows choosing the starter dependencies from a well-organized list: developer tools, web, template engines, security, SQL, NoSQL, Messaging, I/O, OPS, Observability, Testing, and Spring Cloud.
For example, for building Web applications with Spring MVC and Tomcat server, Initializr automatically adds the spring-boot-starter-web starter dependency, which in turn contains references to the set of compatible jars.
In addition to the official Spring Boot starters, there are also third-party starter projects usually named thirdpartyproject-spring-boot-starter.
6. What is the structure of the Spring Boot project?
Spring Boot does not require a specific code layout to work, nevertheless following the "best practices" may solve a lot of troubles in the future. The typical project layout looks as below:
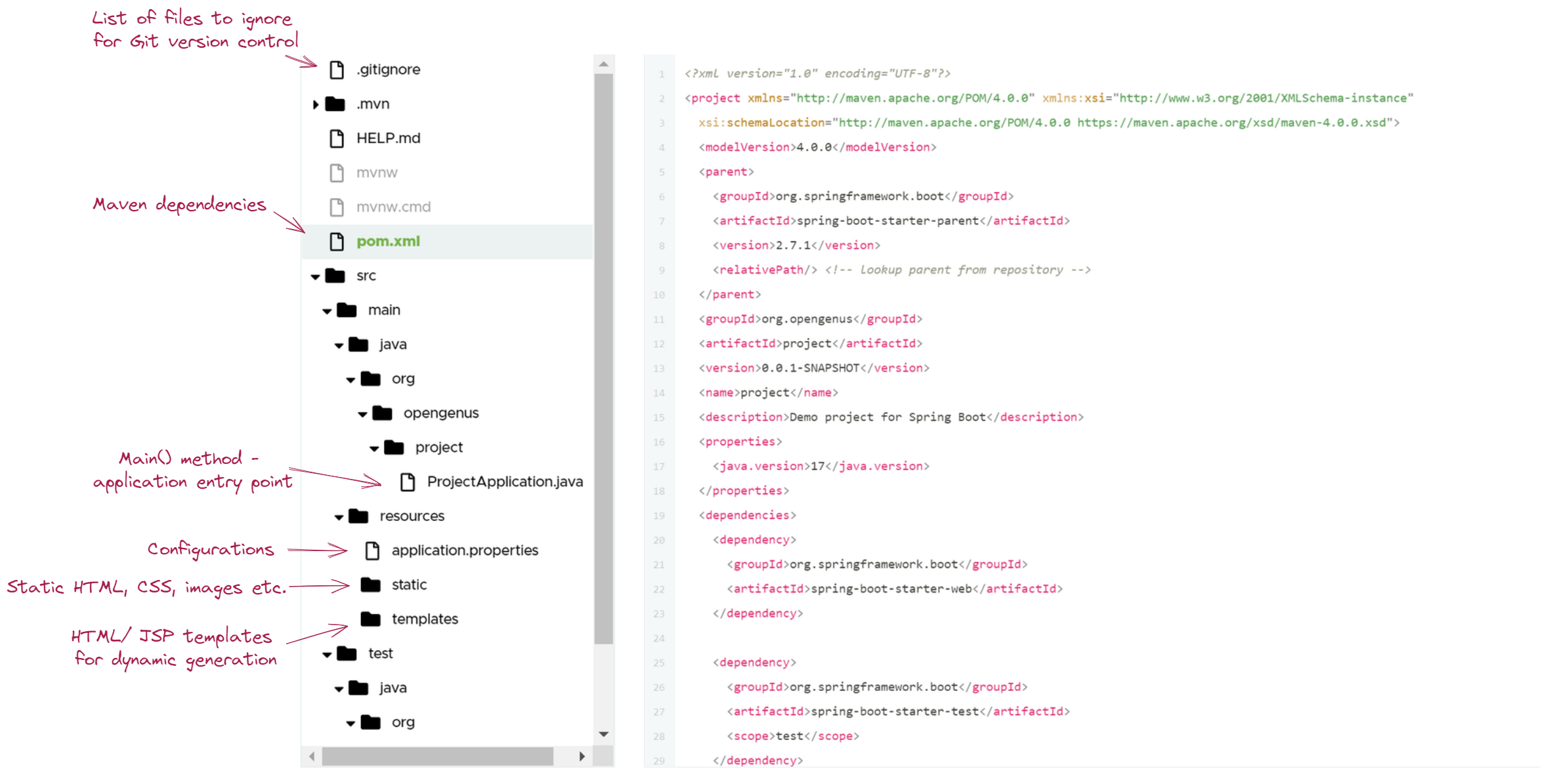
7. Tell me about the Spring Boot properties file
The application.properties file inside the src/resources folder is a convenient way to consolidate application configurations. For example, line server.port = 9999 changes the default port of the application from 8080 to 9999.
It accepts a large list of configurations from database to security setups, even Hibernate settings can be added with the spring.jpa.properties.hibernate header. For example, spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true will command Hibernate to format SQL statements.
Of course, application.properties is not the only way to introduce configurations, Spring Boot also supports YAML files, externalized properties, and environment-specific property files.
8. What profiles are used for?
Enterprise applications undergo different production stages: development, testing, staging, production, user acceptance testing, etc. Instead of the editing configuration file for each of the development environments, Spring Boot allows to create corresponding profiles and simply choose the profile for the current environment.
In practice, developers add configuration files application-dev.properties, application-test.properties, application-prod.properties etc. and set active profile in the main configuration file application.properties with the spring.profile.active line.
In addition to properties settings, any @Component, @Configuration or @ConfigurationProperties can be marked with @Profile annotation to limit when it is loaded.
9. What YAML files are for in Spring Boot?
Spring Boot also allows configuring the application with YAML (literally Yet Another Markup Language) files. This format is considered human-friendly and its hierarchical structure allows to avoid repetition.
So, for example, with profiles, instead of copy-pasting property files and changing details for a different environment, all settings can be structured in a single YAML file. Spring Boot will automatically load application.yaml file from the classpath (folder inside the project where resources are placed) or from the current directory.
Workflow of Spring Boot application
10. How does Spring Boot application work?
Sometimes, Spring Boot is referred to as "magic" because of the amount of work it does behind the scenes. On application startup, Spring Boot automatically checks the environment - what dependencies are added to the project and what annotations are present, then it configures the application and creates the initial context. The entry point of the application is defined with the @SpringBootApplication annotation that triggers @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration, and @ComponentScan annotations.
@Configurationallows writing annotated configurations inside a class instead of XML files@ComponentScanallows to scan classes and Spring components like@Component,@Service,@Repository,@Controllerand automatically register them as Spring beans@EnableAutoConfigurationenables Spring Boot autoconfiguration
11. Does Spring Boot generate code?
No, it is a common misconception. Instead, Spring Boot leverages configuration features of Spring along with dependency resolution of Maven or Gradle and automatically configures beans in the Spring application context.
12. What is the component in Spring Boot?
Spring Boot automatically initializes the core Spring application context, where @Component is the central annotation that indicates custom bean classes to instantiate in the Spring context for later use. The @Component is the meta-annotation for more specialized @Service, @Repository, and @Controller annotations.
13. What is the @Service annotation used for?
@Service is the org.springframework.stereotype annotation like @Repository or @Controller, it indicates that an annotated class is a "Service" regarding the business logic. Technically though it has the same behavior as the more general @Component.
14. How to handle application events with Spring Boot?
Spring Boot supports built-in Spring Framework events like ContextRefreshedEvent, ContextStartedEvent, or ContextClosedEvent and methods to listen for events annotated with the @EventListener annotation.
In additional to those, Spring Boot adds events related to the application lifecycle: ApplicationStartingEvent, ApplicationStartedEvent, ApplicationReadyEvent, ApplicationFailedEvent, WebServerInitializedEvent etc., and SpringApplication.addListeners() method to register event listeners even before the ApplicationContext is created.
15. How to reduce the loading time of the Spring Boot application?
Scanning for and instantiating Spring components can take a considerable amount of time, Spring Boot allows lazy initialization to speed up the application startup process, so the beans are instantiated only when they are needed.
However, lazy initialization can lead to unexpected problems during the runtime of the application, including misconfigured beans or running of memory JVM, so by default lazy initialization is turned off.
16. What is the use of the Spring Boot Developer Tools?
Spring Boot application takes some time to start, this slows down the developing process with repetitive change-restart cycles. The Spring Boot Developer Tools introduces a nice feature to automatically restart the application whenever it detects changes in the files on the classpath. It is turned on simply by adding the spring-boot-devtools dependency.
Web development with Spring Boot
17. What are the differences between @Controller and @RestController?
In Spring MVC (Model-View-Controller) web framework, @Controller represents classes that manage data in the Model interface and provide it to the presentation layer of the application.
Usually, the @Controller annotation is used in combination with the @RequestMapping annotation for handling incoming requests in web applications:
- DispatcherServlet intercepts the request
- Map request URI to one of the
@RequestMappinginside the@Controller - Execute the corresponding method
- Build response entity
- Convert the response entity to the type specified by the request
- Return response to the request
The @RestController is a convenient annotation that includes @Controller and @ResponseBody. It indicates that the data returned by a method in @RequestMapping will be written straight into the response body instead of rendering a template, which is used for building REST services.
18. Tell me about the @RequestMapping annotation in Spring Boot
The @RequestMapping annotation maps methods in the controller beans to the incoming HTTP requests. For example, @RequestMapping("/") will lead to the starting page of the web application, or http://localhost:8080/ on a local machine. It has optional parameters to specify the path, HTTP request method, headers, and parameters.
For convenient use of the @RequestMapping, Spring Boot also includes separate annotations for HTTP methods: @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, and @DeleteMapping.
19. How to handle request-related errors with Spring Boot application?
Handling exceptions and sending a meaningful response to the client is a good practice for application development. Spring Boot manages exceptions the same way as Spring with the following annotations:
@ControllerAdviceclass handles exceptions globally@ExceptionHandlermethod to handle specific exceptions and send custom responses to the clientResponseStatusExceptionbase class for exceptions associated with specific HTTP response status codes
20. How to customize the default error page in the Spring Boot application?
Spring Boot automatically generates the Whitelabel Error Page to handle errors, this can often be seen when the application does not have an explicit route mapping for the error. The default error page of the Spring Boot can be disabled with the server.error.whitelabel.enabled=false property, but then the default web page of the servlet container will be used. It is possible to add an error page template to the templates folder, it will be automatically picked by the Spring Boot depending on the template engine used, for the Thymelead engine, for example, Spring Boot recognizes the error.html file.
To achieve custom logic for handling errors, the Spring Boot application needs a @Controller class that implements the ErrorController marker interface that identifies that @Controller should be used to render errors.
21. Can Spring Boot be used for reactive web applications?
Spring Boot serves for the building of servlet-based web applications with Spring MVC or Jersey. Since Spring 5.0 it also allows for the building of reactive web applications on the HTTP layer with the Webflux framework. The reactive programming paradigm helps to implement non-blocking, asynchronous, and event or message-driven data processing. Spring WebFlux supports functional and annotation-based configuration, and the idea is to manage incoming requests as a series of events in an event loop instead of assigning each request a separate thread that has to wait for the worker threads to finish.
22. Spring Boot supports integration with what messaging systems?
Messaging is a technique for communicating between applications that has a message broker in an intermediate layer between message producers and consumers. Spring framework, and Spring Boot support messaging with JMS API between Java applications and Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (Spring AMQP). Spring Boot supports RabbitMQ, Apache Kafka, and RSocket messaging brokers.
23. How to enable HTTP/2 support in Spring Boot?
Spring Boot supports both HTTP/2 over TLS (h2) and HTTP/2 over TCP (h2c), to enable it is enough to add server.http2.enabled = true to the configuration file. Both the web server and Java version must support HTTP/2, which is true for Tomcat 9.0.x and JDK9+.
24. How to sign in with the Google account to the Spring Boot application?
Spring Security supports the OAuth2 authorization framework that allows end-users to log in using their own Google accounts instead of application-managed credentials.
Setting up includes the following steps:
- Create Google OAuth credentials for the application
- Add OAuth2 dependency to the project
spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client - Add OAuth2 configuration -
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.google.client-id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_IDandspring.security.oauth2.client.registration.google.client-secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRETto the application propetries file - Configure authorized redirect URIs on the Google Credentials settings or with the application routing
25. Is Spring Boot only for web development?
No, the Spring Boot allows to run applications without a web server, to do so either exclude all (transitive too) dependencies for the web server or programmatically customize SpringApplication with the setWebApplicationType(WebApplicationType.NONE) method.
Data storage with Spring Boot
26. What options does Spring Boot support for the data persistence?
Spring Boot allows a variety of connectivity options with both SQL and NoSQL databases: from the embedded in-memory H2 Database, different relational databases, and ORMs, to popular NoSQL Redis and MongoDB solutions.
Important Spring framework that Spring Boot uses is the Spring Data JDBC, which helps to implement access to the relational databases but does not provide features for caching of lazy loading. Probably more popular is the Spring Data JPA, which allows the implementation of CRUD operations with Repository interfaces. Spring Boot with Spring Data JPA automatically configures and uses Hibernate ORM to run JDBC requests.
27. How do repositories work in Spring Boot?
Spring Data repository abstraction helps to implement data access layers. It includes Repository interfaces for a variety of purposes, for example, CrudRepository provides CRUD functionality for the managed entity class, and the JpaRepository extends CrudRepository and provides persistence technology-specific capabilities.
Spring Boot automatically detects and handles Spring repositories in the same package or sub-package with the main Spring Boot application class.
Application health with Spring Boot
28. What is the Spring Boot Actuator?
Spring Boot Actuator allows to collect the operational data about running application and expose it on HTTP endpoints. The actuator is turned on by adding spring-boot-starter-actuator dependency to the project. It allows to monitor the application health and metrics and has several customizable endpoints: beans, health, caches, httptrace, sessions, and many others.
29. How to view log information with Spring Boot?
Spring Boot uses Apache Commons Logging for all internal logging and also provides configurations for Java Util Logging, Log4J2, and Logback loggers.
By default Spring Boot only shows INFO, ERROR, and WARN log messages, to view more detailed information, either start the application with a --debug or --trace flag, or set debug-true in the application.properties file.
For more fine-grained log level settings, it is enough to add a logger configuration file to the project classpath, so the Spring Boot will automatically load it.
Application deployment
30. How to deploy Spring Boot Project?
The Spring Boot allows building an application into a JAR or WAR file that includes all verified nested dependencies, thus allowing to run an application in every environment that has a JVM (Java Virtual Machine) and skip the usual steps of application deployment.
Spring Boot executable jars are designed for and easy to deploy with the most popular cloud providers such as Heroku, AWS, Google Cloud, and Kubernetes. It is also possible to make fully executable applications run it as a system service on Unix systems, or use Windows Service Wrapper and run the application as a service on Windows.
Multiple choice questions
1. Which annotation does not belong to Spring Boot?
2. What of the template engines Spring Boot does not support auto-configuration for?
3. What annotation must be placed to indicate the database persistence object?
4. How can we change the port of the embedded Tomcat server in Spring Boot?
5. What is the relation between @Component, @Service, and @Repository?
6. What is the purpose of the message.properties files in the src/main/resources folder of the Spring Boot project?
7. Spring Boot provides integration with the following JSON mapping libraries except?
8. How to get application context with Spring Boot?
9. What is the default user name for the login page generated by Spring Security?
10. How fields annotated with @Transient annotation are cached?
11. What Log levels are not printed to the console in the default Spring Boot application configuration?
12. Which of the annotations below does not belong to Spring?
13. Spring Boot is developed by?
14. What is the minimum Java version needed for Spring Boot?
15. What is the Starting point of a Spring Boot Application?
16. Which of the following is true for the @Autowired annotation?
17. How to test Spring Boot application without starting the web server?
18. What is not a convenience annotation for @RequestMapping?
19. Why starting up a Spring Boot project takes minimum efforts and configurations?
20. What are the Spring beans scopes?
With this article at OpenGenus, you must have good practice with Interview questions on Spring Boot.