Types of Bitcoin Wallets
In this article, we learn about the major types of Bitcoin wallets. Software, Hardware, and Paper Wallets and their applications, pros and cons.
Table of contents.
- Introduction.
- Bitcoin Wallets.
- Software Wallets.
- Hardware Wallets.
- Paper Wallets.
- Summary.
- References.
Introduction
On the Bitcoin blockchain, a wallet with an address is the main interface used to interact with the blockchain, on the Ethereum blockchain, accounts with addresses are used to initiate transactions and execute smart contract code.
A blockchain wallet just like a hard wallet is used as a store of value. In the case of hard wallets, they store hard notes and probably coins, on the other hand, blockchain address just store data that cannot be corrupt. Blockchain participants all require a bitcoin wallet address or an Etherium account to send and receive cryptocurrency. The wallet can manage multiple cryptocurrencies.
In this article, we learn about the different blockchain wallets and their use cases, and some of their features.
There exist three major categories of blockchain wallets, these are; hardware which is the most secure, software which is the most convenient for day-to-day transactions, and paper wallets. Based on how they are used and their functionalities they are further categorized into hot or cold.
Types of Bitcoin Wallets are:
- Bitcoin Wallets
- Software Wallets
- Hardware Wallets
- Paper Wallets
Bitcoin Wallets.
We know that a blockchain's main component is cryptography, we have seen how to generate public and private key pairs. These are used to generate a unique Bitcoin address. The address is what a sender A will embed in a transaction declaring that amount X of funds now belong to recipient B. Also remember, public keys are shared and private keys are stored secretly, they should only be known to the owner.
A seed is also generated during the creation of a wallet, mnemonics are used for displaying the seed in form of words; An example of a seed phrase is shown below;
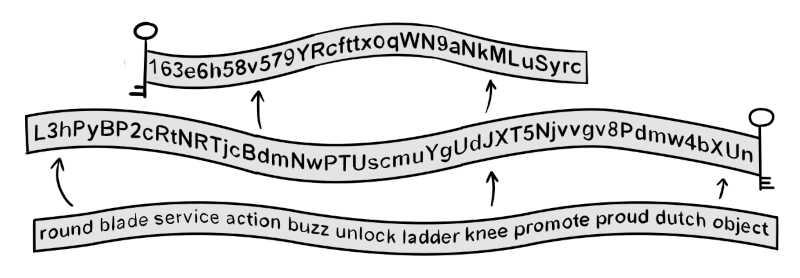
The seed is used to generate keys that will be used during a transaction between parties. This is referred to as hierarchical determinism, which means that once a transaction is completed, a new public key is generated. This ensures safety and anonymity for a participant.
Participants use the seed to restore access to a Bitcoin wallet and therefore it is important to keep it a secret.
Software Wallets.
These are wallets implemented using software, they can be mobile-based, web-based, and desktop based. Software wallets are considered convenient, for the everyday user who conducts business on the blockchain, an app or desktop app or a website is easily accessible.
Mobile Wallets
These consist of apps that can be found on the play store or apple store downloaded and installed. Just like leather wallets that are carried in back pockets, mobile blockchain wallets are carried on an app. Some apps also go a step further to make sure the transaction is as seamless as possible by using near-field communication, this allows the 'tap tp pay' feature.
Mobile wallets rely on a small number of blockchain nodes for the verification and validation of transactions. While this provides such convenience, this structure is not what Bitcoin is since it is no longer a distributed ledger because only a small number of nodes participating in the transactions.
It is common for users to store Bitcoins that they are going to use in mobile wallets and then store the rest in a hardware wallet(cold storage). This is a safety measure against scammers.
Examples of mobile wallets include; coin base wallet, Zengo, Crypto.com, Binance wallet, etc.

Web-based wallets
These are just websites that act as wallets, they allow users to manage their Bitcoins on the blockchain. We-based wallets are managed by third parties, this means these parties can access the private keys since all data is on their servers. And remember, whoever controls knows your private key owns your funds.
Web-based wallets can also integrate and synchronize with mobile wallets. This offers convenience to users since all that is needed to access the funds is just an internet connection.
Most web-based wallets are associated with crypto exchanges which are third parties that can decide to get away with your funds. Also, web-based wallets require authentication to log in, this authentication is based on email and passwords which is hackable.
Examples of mobile wallets include; Electrum, Coinbase Wallet, Crypto.com Wallet, Binance Wallet, etc.
Desktop Wallets
These wallets require one to download the software from the official website. They are considered more secure than the previous two since the software on your desktop machine can be air-gapped preventing external access.
However, if the desktop computer is connected to the internet, there is a high possibility of data exchange between third-party servers and the desktop.
Desktop wallets come in a lot of variety depending on the use., it can be convenience, anonymity, security, etc.
We can also opt to spare some disk space and bandwidth to run a bitcoin node, this allows us control over our transactions, in that we can process our transactions and keep our funds safe since there are no third parties.
Examples of desktop wallets include; Atomic, Exodus, Guarda, Jaxx Liberty, Electrum, etc.
Hardware wallets.
These are actual tangible devices that look like USB flash disks. These are considered the most secure, since private keys are stored on a secure tangible device, just like a hard wallet with hard currency, they cannot be hacked or infected by computer viruses although once lost so are the funds.
There are also hardware wallets with screens that are very convenient for verifying transactions. For hardware wallets, we should make sure we buy the correct one from a trustworthy vendor since any mistake can result in the loss of funds.
Examples of hardware wallets include; Ledger Nano S, Trezor Model One, SafePal S1, Steel Bitcoin Wallet, Trezor Model T-Next Generation, etc

Paper wallets
Finally, we have paper wallets, these are just like they sound, they are hard copy papers that contain the public address for receiving bitcoins and a private key that allows the owner to spend or send bitcoins stored in the address.
They are often in QR-code format meaning we can use a scanner to initiate transactions, this is very convenient. An example of a paper wallet can be generated here.
The following is an image of a paper wallet;

After generating the keys, we can then print a tamper-resistant hard copy. This is similar to cash, a piece of paper representing a specific value, and just like cash, it is prone to wear and tear, getting wet, getting burnt, stolen, or lost. This is solved through lamination and safe storage.
Paper wallets are secure since they are offline and tangible like hard cash, except for the part where we use a third party to generate the keys. To remove third parties, we can compile the source code locally and use it to generate wallets.
Summary
Bitcoin wallets are the only interface participants can interact with the Bitcoin blockchain.
The main purpose of Bitcoin is the storage and transfer of value between parties.
Bitcoin wallets do not store actual funds rather they store keys. These keys are the ones that are used to access funds on the distributed ledger.
There are three major types of crypto wallets, software, hardware, and paper. Software offer convenience in day-to-day transactions, they can be web-based, desktop, or mobile-based, hardware wallets are mainly used to store Bitcoins safely and cannot be hacked although once lost, so are the funds. Paper wallets are also used but have become obsolete since they wear and tear and once the QR code becomes unreadable, the owner faces the risk of losing funds.