
Open-Source Internship opportunity by OpenGenus for programmers. Apply now.
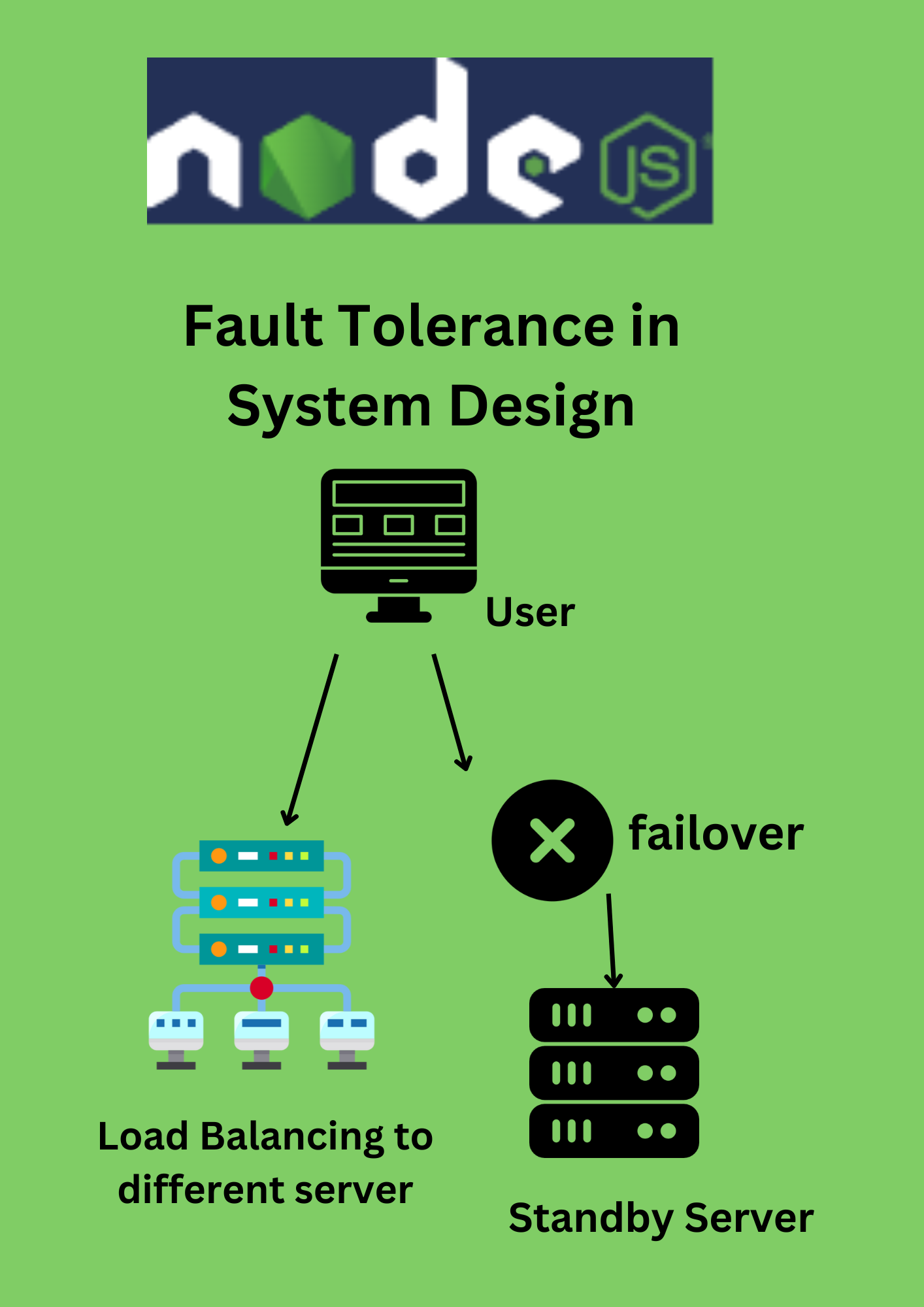
As technology continues to advance, we rely more and more on computer systems to store, process, and transmit important information. However, these systems are not perfect and can sometimes fail due to hardware, software, or network problems. That's where fault tolerance comes in. Fault tolerance refers to a system's ability to continue operating even when one or more components fail.
To achieve fault tolerance, system architecture uses a variety of techniques. One of the most common techniques is redundancy, which means that a system has multiple components that perform the same function. For example, a server cluster may have multiple servers, each with a copy of the same data, so that if one server fails, the others can take over. This way, even if one component fails, the system can continue operating.
Now Redundancy is one of the method to deal with failure, there are others which are used across the industry in desigining different system according to the need.
Let's go through different methods that are in use:
Redundancy
As dicussed earlier this method involves having multiple components in the system that can perform the same function. In the event of a failure, the backup component takes over, and the system can continue operating. Examples of redundancy techniques include:
- Hardware redundancy: This involves having multiple copies of hardware components, such as servers or storage devices, in the system.
- Software redundancy: This involves replicating software components, such as applications or databases, across multiple systems.
Monitoring and detection
To achieve fault tolerance, it's important to monitor the system for errors or failures.
Techniques for monitoring and detection include:
- Error detection codes: These are used to detect errors in data transmission, such as parity or checksums.
- Heartbeat monitoring: This involves regularly checking the status of system components to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Failure prediction: Using machine learning algorithms to predict and prevent failures before they happen.
Isolation
Isolation techniques can be used to prevent faults in one part of the system from affecting other parts. Examples of isolation techniques include:
- Virtualization: This involves running multiple virtual machines on a single physical server, each with its own isolated environment.
- Sandboxing: This involves running an application in a secure, isolated environment to prevent it from affecting other applications or the system as a whole.
- Graceful degradation: This involves reducing the system's functionality in the event of a failure, rather than completely shutting down. Examples of graceful degradation techniques include:
- Read-only mode: This involves allowing users to read data from the system, but not make changes to it.
- Reduced capacity mode: This involves limiting the number of users or transactions that can be processed by the system to prevent overload.
Overall, achieving fault tolerance requires a combination of techniques, and the specific methods used will depend on the system's requirements and architecture. By implementing these techniques, designers can ensure that the system continues to operate even in the face of failures or errors, improving its reliability and availability.
Once a fault has been detected, the system needs to be able to recover from it. This may involve switching to a redundant component, restoring data from a backup, or reconfiguring the system to work around the fault. This is known as fault recovery.
Some of the fault recovery options are :-
- Rollback and replay: This involves restoring the system to a previous known good state and replaying the transactions that occurred since that point.
- Checkpointing: This involves periodically saving the system's state so that it can be restored in the event of a failure.
- Automatic failover: This involves automatically switching to a redundant component in the event of a failure.
System Design of an application involving fault tolerance
Social Media Platform
- Business Requirements :-
- High availability: The social media platform should be available 24/7/365
- High scalability: The system should be able to handle a large number of users and posts
- Fault tolerance: The system should be able to recover from hardware or software failures without downtime or data loss
- Data privacy: The system should protect user data and prevent unauthorized access
- Architecture :-
- Load Balancer: To distribute traffic across multiple instances of the application server, a load balancer can be used. This will ensure that users are always directed to an available instance of the application server.
- Application Server Cluster: Multiple instances of the application server will be deployed in a cluster. The server instances will communicate with each other to synchronize data and maintain consistency. If one server fails, the other servers will continue to handle user requests, ensuring that the platform remains available.
- Database Cluster: The database will also be deployed in a cluster to ensure high availability and fault tolerance. The cluster will consist of multiple nodes, and data will be replicated across the nodes for redundancy and resilience.This means that if one database node fails, the data can be retrieved from another node, ensuring that user data is not lost.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN can be used to improve performance and reduce the load on the application server. The CDN will store frequently accessed static content, reducing the number of requests to the application server.If one CDN server fails, requests will automatically be directed to another server, ensuring that users can still access the platform.
- Backup and Recovery: Regular backups will be taken of the database and application server. In the event of a failure, the system
By incorporating these fault-tolerant mechanisms, the social media platform can remain available and functional even in the face of hardware or software failures.
In conclusion, fault tolerance is an important consideration in system design. By using techniques like redundancy, monitoring and detection, fault recovery, isolation, and graceful degradation, designers can create systems that are able to continue operating even in the face of faults or errors. This is essential for systems that need to provide high levels of reliability and availability, and it ensures that our important data and systems are protected even when problems occur.
