
Open-Source Internship opportunity by OpenGenus for programmers. Apply now.
Reading time: 15 minutes
A field programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by anyone for various purposes like hardware stimulation. FPGA is defined by two keywords namely field programmable and gate array.
Accordingly, FPGA means:
-
field programmable: An FPGA is designed to be easily reconfigured by developers, designers or customers. Verilog Hardware Description Language (VHDL) is used as the programming language for FPGA programming.
-
gate array: An FPGA consists of an array of programmable logic gates such as AND, OR, XOR, NOT, memory elements, DSP components and reconfigurable interconnects which are to connect logic gates together for performing a specific function.
An FPGA looks like:
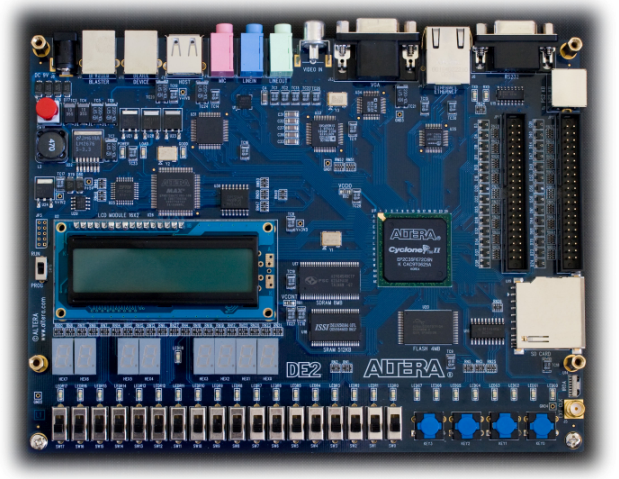
FPGA applications
An FPGA can be used as follows:
-
For design prototyping
-
For emulation
-
As hardware accelerator
-
In place of ASIC
- Less time to market
-
Complete System on Chip (SoC) solution
-
An FPGA can be used to implement any Digital Signal Processing Algorithm such as:
- Bluestein's FFT algorithm
- Fast Fourier transform
- Prime-factor FFT algorithm
- Gerchberg–Saxton algorithm
and many other algorithms
- FPGA can also be used to stimulate any hardware of your choice
FPGA Architecture
The most common FPGA architecture consists of:
- array of logic blocks
- Hard blocks like high speed multi-gigabit transceivers
- Clocking circuitry
FPGA manufacturers
Major manufacturers of FPGA are:
- Xilinx
- Altera (part of Intel)

Why to use FPGA?
Field Programmable Gate Array are to be used because of the following reasons:
- Fast-turnaround prototype implementation
- Supported by CAD/EDA tools
- High density
- High speed
- Programmable and versatile
- Flexible
- Reusable
- Large amounts of logic gates, registers, RAM and routing
- resources
- Quick time-to-market
- SRAM FPGA provide the benefits of custom CMOS
