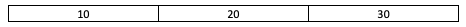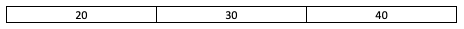Open-Source Internship opportunity by OpenGenus for programmers. Apply now.
Reading time: 15 minutes
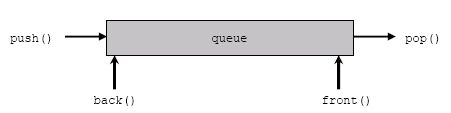
The queue in the STL of C++ is a dynamically resizing container to implement the queue data structure. It is a sequential linear container which follows the First In First Out(FIFO) arrangement.
Definition in <queue>
std::queue is defined as follows under <queue> header file:
template <class T, class Container = deque<T> > class queue;
Declaration
A queue with name a storing integers is declared as follows:
queue<int> a;
Functions
Assume the queue a to be:
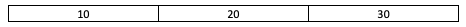
and the queue b to be:
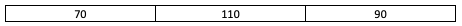
The following functions are defined under the <queue> header file:
- a.empty(): Returns true if the queue is empty, false otherwise.
- a.size(): Returns an integer indicating the size of the queue a.
- a.swap(b): Swaps the contents of queue a with queue b.
- a.emplace(x): Places the element x at the back of the queue a.
- a.front(): Returns a reference to the first element of the queue a.
- a.back(): Returns a reference to the last element of the queue a.
- a.push(x): Inserts the element x at the back of the queue a.
- a.pop(): Removes the element x at the front of the queue a.
For the above queue a, the function returns false.
For the above queue a, the function returns the integer 3.
For the above example, if the function is called, queue a becomes:
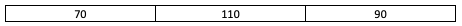
And queue b becomes:
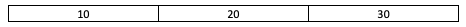
For the queue a, if the function a.emplace(40) is called, a becomes:

For the above queue a, the function returns the integer 10.
For the above queue a, the function returns the integer 30.
For the queue a, if the function a.push(40) is called, a becomes:

For the queue a, if the function a.pop() is called, a becomes:

Illustration of Queue
// C++ code to illustrate queue in Standard Template Library (STL)
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
void display(queue <int> q)
{
queue <int> c = q;
while (!c.empty())
{
cout << " " << c.front();
c.pop();
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main()
{
queue <int> a;
a.push(10);
a.push(20);
a.push(30);
cout << "The queue a is :";
display(a);
cout << "a.empty() :" << a.empty() << "\n";
cout << "a.size() : " << a.size() << "\n";
cout << "a.front() : " << a.front() << "\n";
cout << "a.back() : " << a.back() << "\n";
cout << "a.pop() : ";
a.pop();
display(a);
a.push(40);
cout << "The queue a is :";
display(a);
return 0;
}
\\Console output
The queue a is : 10 20 30
a.empty() :0
a.size() : 3
a.front() : 10
a.back() : 30
a.pop() : 20 30
The queue a is : 20 30 40
State of Queue a after each iteration: