Open-Source Internship opportunity by OpenGenus for programmers. Apply now.
Reading time: 30 minutes | Coding time: 10 minutes
Given a binary search tree and a integer k our task is to find out sum of all the elements which is less or equal to the k th smallest element in binary search tree.
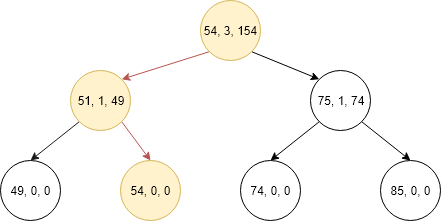
For example for given below binary search tree and k=3.
Explanation: so here in above example k th smallest element is 52 and sum of all the elements which is less or equal to 52 is 152.
We will explore two approaches:
- Naive approach O(N)
- Efficient approach O(log N)
Naive Approach
This is a simple approach this takes O(n) time and O(1) extra space.
Algorithm:
- Do inorder traversal of binary search tree and and count the visited elements and add all the elements to a variable.
- when count is equal to k return the variable having sum of all the elements until that point and that is the output.
Implementation of above algorithm is given below.
// c++ program to find Sum Of All Elements smaller
// than or equal to Kth Smallest Element In BST
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Binary tree Node */
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* left, * right;
};
// utility function new Node of BST
struct Node *createNode(int data)
{
Node * new_Node = new Node;
new_Node->left = NULL;
new_Node->right = NULL;
new_Node->data = data;
return new_Node;
}
// A utility function to insert a new Node
// with given key in BST and also maintain lcount ,Sum
struct Node * insert(Node *root, int key)
{
// If the tree is empty, return a new Node
if (root == NULL)
return createNode(key);
// Otherwise, recur down the tree
if (root->data > key)
root->left = insert(root->left, key);
else if (root->data < key)
root->right = insert(root->right, key);
// return the (unchanged) Node pointer
return root;
}
// function return sum of all element smaller than
// and equal to Kth smallest element
int ksmallestElementSumRec(Node *root, int k, int &count)
{
// Base cases
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (count > k)
return 0;
// Compute sum of elements in left subtree
int res = ksmallestElementSumRec(root->left, k, count);
if (count >= k)
return res;
// Add root's data
res += root->data;
// Add current Node
count++;
if (count == k)
return res;
// If count is less than k, return right subtree Nodes
return res + ksmallestElementSumRec(root->right, k, count);
}
// Wrapper over ksmallestElementSumRec()
int ksmallestElementSum(struct Node *root, int k)
{
int count = 0;
ksmallestElementSumRec(root, k, count);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
Node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 54);
root = insert(root, 51);
root = insert(root, 49);
root = insert(root, 52);
root = insert(root, 75);
root = insert(root, 74);
root = insert(root, 85);
int k = 3;
cout <<"Sum of k smallest elements is " << ksmallestElementSum(root, k) <<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Sum of k smallest element is 152
Explanation:
- First of all go to the left most element and add to the a variable is out case it is res and increment the counter by 1. so now res = 49 and count = 1. Now check if count is equal to three no then go the another element.
- Now current node is 51 add it to the res and increase counter by 1 now res = 100 and count = 2 check if count if equal to k no then go to the another element.
- Now current node is 52 add it to the res and increase counter by 1 now res = 152 and count = 3 check if count if equal to k yes then return res and it is required output.
Efficient Approach
Here we use augmented tree data structure to solve this problem efficiently in O(h) time [ h is height of Binary Search Tree ] .
Structure of Augmented Tree
Binary Search Tree Node contain to extra fields : lCount , Sum
For each Node of Binary Search Tree
lCount : store how many left child it has
Sum : store sum of all left child it has
Insertion In Augmented Tree
- When we insert a node in this tree if key value is less then current node value then add key value to the sum of the current node and increment lcount by 1 of that node. if key value is greater than current node then go to the right similar to binary tree.
- Do above process to all he nodes which come in the way till you don't reach the insertion point.
For example binary search tree given below we want insert 49 in it.
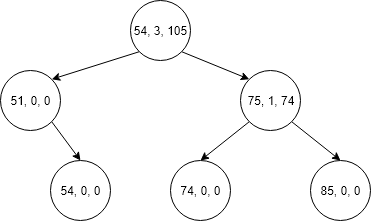
Now tree becomes as shown below.
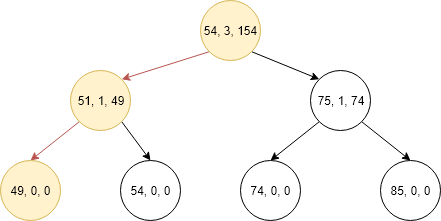
Algorithm for finding sum of k smallest elements in Binary Search Tree
Find Kth smallest element
[ temp_sum store sum of all element less than equal to K ]
ksmallestElementSumRec(root, K, temp_sum)
IF root -> lCount == K + 1
temp_sum += root->data + root->sum;
break;
ELSE
IF k > root->lCount // Goto right sub-tree
temp_sum += root->data + root-> sum;
ksmallestElementSumRec(root->right, K-root->lcount+1, temp_sum)
ELSE
// Goto left sun-tree
ksmallestElementSumRec( root->left, K, temp_sum)
Implementation of above algorithm is given below.
// C++ program to find Sum Of All Elements smaller
// than or equal t Kth Smallest Element In BST
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Binary tree Node */
struct Node
{
int data;
int lCount;
int Sum ;
Node* left;
Node* right;
};
//utility function new Node of BST
struct Node *createNode(int data)
{
Node * new_Node = new Node;
new_Node->left = NULL;
new_Node->right = NULL;
new_Node->data = data;
new_Node->lCount = 0 ;
new_Node->Sum = 0;
return new_Node;
}
// A utility function to insert a new Node with
// given key in BST and also maintain lcount ,Sum
struct Node * insert(Node *root, int key)
{
// If the tree is empty, return a new Node
if (root == NULL)
return createNode(key);
// Otherwise, recur down the tree
if (root->data > key)
{
// increment lCount of current Node
root->lCount++;
// increment current Node sum by adding
// key into it
root->Sum += key;
root->left= insert(root->left , key);
}
else if (root->data < key )
root->right= insert (root->right , key );
// return the (unchanged) Node pointer
return root;
}
// function return sum of all element smaller than and equal
// to Kth smallest element
void ksmallestElementSumRec(Node *root, int k , int &temp_sum)
{
if (root == NULL)
return ;
// if we fount k smallest element then break the function
if ((root->lCount + 1) == k)
{
temp_sum += root->data + root->Sum ;
return ;
}
else if (k > root->lCount)
{
// store sum of all element smaller than current root ;
temp_sum += root->data + root->Sum;
// decremented k and call right sub-tree
k = k -( root->lCount + 1);
ksmallestElementSumRec(root->right , k , temp_sum);
}
else // call left sub-tree
ksmallestElementSumRec(root->left , k , temp_sum );
}
// Wrapper over ksmallestElementSumRec()
int ksmallestElementSum(struct Node *root, int k)
{
int sum = 0;
ksmallestElementSumRec(root, k, sum);
return sum;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
Node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 12);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 22);
int k = 3;
cout<<"Sum of k smallest is " << ksmallestElementSum(root, k) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Sum of k smallest element is 152
Explanation:
- First of all go to the root and compare k with lcount + 1 if it is equal then temp_sum = 208 and return otherwise if k<lCount then go the left child of the root.
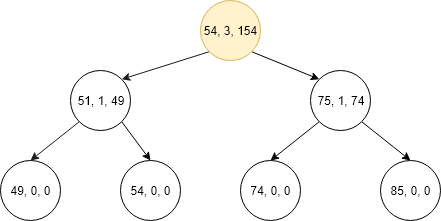
- Now compare the lCount + 1 of current node with k if it is equal then temp_sum = 100 and return if k>lCount the go to right and temp_sum = 100 and k = 1.
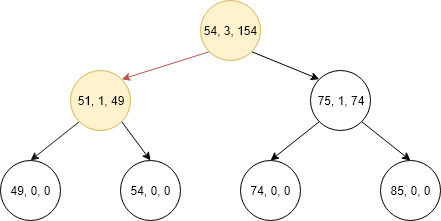
- Now again compare lCount + 1 with k if it is equal then temp_sum = 152 and return.