Open-Source Internship opportunity by OpenGenus for programmers. Apply now.
In this article, we have explored the different ways of defining a 2D array in Python. We have explored three approaches:
- Creating a List of Arrays
- Creating a List of Lists
- Creating 2D array using numpy
Some terminologies in Python:
Array: An array is a collection of homogeneous elements (i.e. belonging to the same data type) that are stored in contiguous memory locations. In Python, there is a module ‘array’ that needs to be imported to declare/use arrays.
List: A list in Python is collection of elements that can belong to different data types. So, a List can be an array if the user chooses to store only homogeneous elements in it. There is no need to explicitly import a module for declaration of Lists.
So, what are 2D arrays/lists?
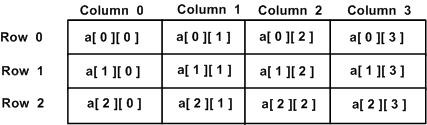
2D arrays/lists can be defined as an array/list of arrays/lists. 2D arrays are also called 'Matrices'.
Creating a List of Arrays:
Syntax of defining an array in python:
import array as arr #imports array module
a = arr.array(‘i’,[1,2,3,4]) #defines a 1D array of integer type
NOTE: You need to mention the data type of the elements and if an element of different data type is inserted, an exception “Incompatible data types” is thrown.
Let’s create a 3*3 matrix(i.e. 2D array)
import array as arr #imports module
a = [] #defining an empty list
for i in range(0,3): #i iterates from 0 to 3
row = arr.array(‘i’) #defining an array
for j in range(0,4): #j iterates from 0 to 4
row.append(i*4+j) #row-wise position is appended
a.append(row) #row array is from the end added to the list 'a'
print(a)
Output: [array('i', [0, 1, 2, 3]), array('i', [4, 5, 6, 7]), array('i', [8, 9, 10, 11])]
Creating a List of Lists:
Now, here is a better and easier way to create a 2D array.
There are different ways in which this can be done with Lists and here I will be showing 3 of them.
Method 1:
This is the most simple way.
rows = 3 #value of rows is defined 3
cols = 3 #value of columns is defined 3
mat = [[0]*cols]*rows #2D list initialized with value 0 is defined
print(mat) #contents of the 2D array 'mat' is displayed
Output:
[[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]]
Method 2:
rows = 3 #value of rows is defined 3
cols = 3 #value of columns is defined 3
mat = [[0 for i in range(cols)] for j in range(rows)] #2D stored in 'mat'
print(mat) #contents of the 2D array 'mat' is displayed
Output:
[[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]]
Method 3:
rows = 3 #value of rows is defined 3
cols = 3 #value of columns is defined 3
mat=[] #empty List is defined
for i in range(cols): #i iterates from 0 to value 'cols'
col = [] #empty List is defined
for j in range(rows): #j iterates from 0 to value 'rows'
col.append(0) #0 is added to list 'col'
mat.append(col) #List 'col' is added to List 'mat'
print(mat) #contents of List 'mat' displayed
Output:
[[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]]
Creating 2D array using numpy:
Though we can use the List for the same purpose but it’s slow. Numpy is a pre-defined package in Python used for performing powerful mathematical operations. It provides an array object much faster than traditional Python lists.
- Using numpy.array()
import numpy as np
#initializing 3 different Lists
row1 = [1,2,3]
row2 = [4,5,6]
row3 = [7,8,9]
mat = np.array([row1,row2,row3]) #initializing array with 3 Lists
print(mat) #display contents of List 'mat'
Output:
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]]
- Using numpy.asarray()
#initializing 3 different Lists
import numpy as np
row1 = [1,2,3]
row2 = [4,5,6]
row3 = [7,8,9]
mat = np.asarray([row1,row2,row3]) #initializing array with 3 Lists
print(mat) #display contents of List 'mat'
Output:
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]]
In numpy arrays there are many functions that can be applied for mathematical computations.So, if you wish to explore more on numpy arrays you can refer to this link.
Applications:
The applications of 2D arrays are:
- To represent images and manipulate them
- To represent any 2-D grid
- Used in programming techniques like Dynamic Programming
Exercise Problem:
Write a program that takes the number of rows and the number of columns of the 2D array as input and then takes input row-wise and displays the 2D array as output.
Solution:
rows = int(input("Enter the no. of rows:")) #user input number of rows
cols = int(input("Enter the no. of columns:")) #user input number of columns
mat = [] #defining empty List
print("Enter the elements row-wise:")
for i in range(rows): #i iterates from 0 to value of 'rows'
row = [] #defining empty List
for j in range(cols): #j iterates from 0 to value of 'cols'
row.append(int(input())) #user input is added in List 'row'
mat.append(row) #List 'row' is added in List 'mat'
for i in range(rows): #i iterates from 0 to value of 'rows'
for j in range(cols): #j iterates from 0 to value of 'cols'
print(mat[i][j], end = " ") #display value at ith row and jth column
print() #line change
Output:
Enter the no. of rows: 2
Enter the no. of columns: 4
Enter the elements row-wise:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
Time Complexity:
Worst case time complexity: O(RC)
Average case time complexity: Θ(RC)
Best case time complexity: Ω(RC)
Space complexity: Θ(RC)
Since we are iterating from column to column in every row hence the complexity is rows*columns.
NOTE: ‘R’ is the number of rows and ‘C’ is the number of columns.
