
Open-Source Internship opportunity by OpenGenus for programmers. Apply now.
In this Blog, you are going to learn to design and implement the graph data structure using OOP (Object Oriented Programming) Concepts. We will implement in Java but the ideas are applicable in any language.
First You need to understand What is Graph Data Structure all about? Learn from here
The main components of graph are:
- Vertex/Nodes
- Edges
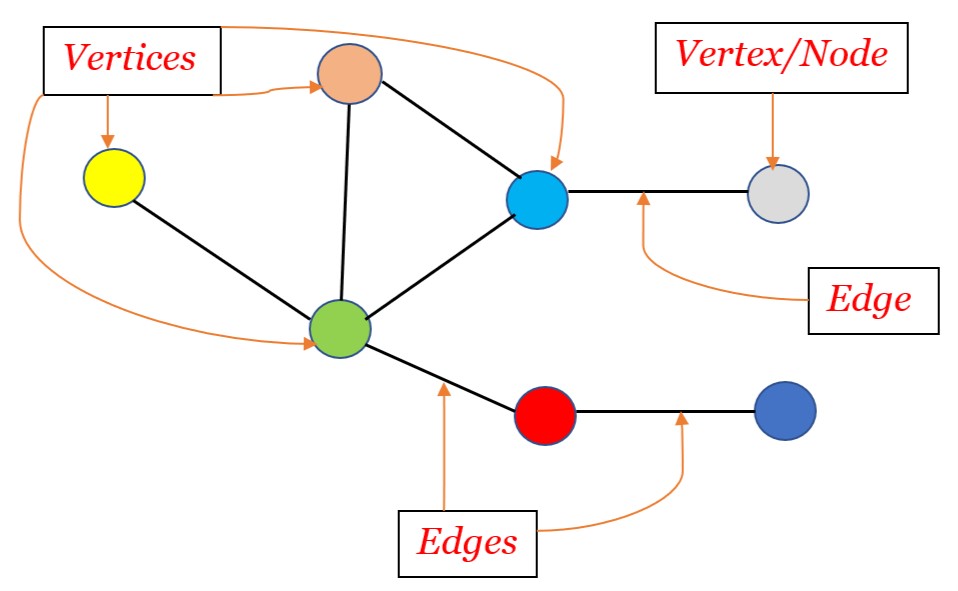
So, how can we initialize these components using Object-Oriented Concepts ?
Let's talk about nodes(vertex),
We need to have multiple nodes in graph having same properties.
To have same properties among different nodes, They should be the Object of the same Class.
So, We need to initialize a Class of Node and need to initialize objects of Node with different attributes but with similar methods(behaviors).
What are the attributes does node have?
- Identifier: Each node should have its identifier(name). Assume cities as nodes of the graph of countries. Then the node have identifier as the city name.
- Neighboring Nodes: Each node stores the identifier of its neighboring nodes connected by Edges.
So, here is the Class(Structure) of Node:
class Node{
String identifier;
ArrayList<> neighbors = new ArrayList<String>();
// Constructor
Node(String Name){
this.identifier = Name;
}
}
Now, What are the methods(behaviors) does node have?
There could be many methods but Let's only talk about the two.
- updateIdentifier: As the name suggests, Using this method, We can update the identifier of the Node.
- addNeighbor: As the name suggests, Using this method, We can add neighbors to the Node's neighbor list.
Let's update the Node class:
class Node{
String identifier;
ArrayList<> neighbors = new ArrayList<String>();
// Constructor
Node(String Name){
this.identifier = Name;
}
public void updateIdentifier(String updatedName){
this.identifier = updatedName;
}
public void addNeighbor(String neighbor){
neighbors.add(neighbor);
}
}
Now every object of the Class Node have specific attributes and methods.
That's how Structure of Node looks like:
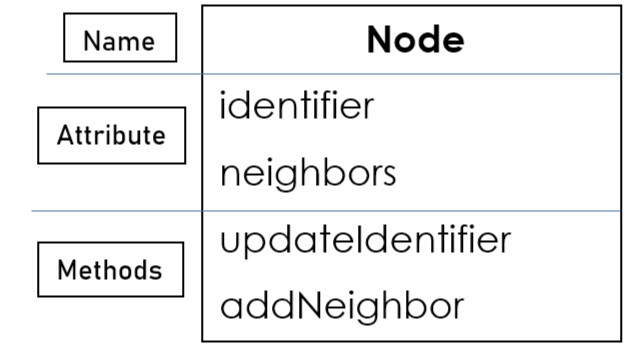
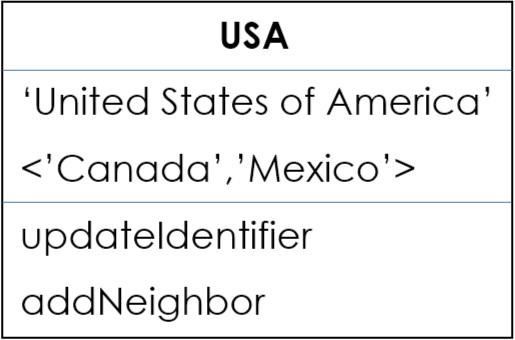
Let's create an object of the Node.
// object initialisation
Node USA = new Node('USA');
// update identifier
USA.updateIdentifier('United States of America');
// adding Neighbors
USA.addNeighbor('Canada');
USA.addNeighbor('Mexico');
Now, Let's learn about the other component i.e. Edge.
Edges connect the two nodes in the graph.
What are the attributes does Edge have?
-
Nodes Connected : This attribute stores the two nodes as source and destination.
-
Weight of the Edge : Suppose in a graph of cities of the country. In this graph, this weight could represent the distance between the cities.
So, here is the Class(Structure) of Edge:
class Edge{
String source,destination;
int weight;
// Constructor
Edge(String sourceNode, String destinationNode, int edgeWeight){
this.source = sourceNode;
this.destination = destinationNode;
this.weight = edgeWeight;
}
}
Now, What are the methods(behaviors) does Edge have?
Let's take three methods for the Edge class:
- updateSource: To update the source of the edge.
- updateDestination: To update the destination of the edge.
- updateWeight: To update the weight of the edge.
Let's update the Edge class:
class Edge{
String source,destination;
int weight;
// Constructor
Edge(String sourceNode, String destinationNode, int edgeWeight){
this.source = sourceNode;
this.destination = destinationNode;
this.weight = edgeWeight;
}
// Methods
public void updateSource(String sourceUpdate){
this.source = sourceUpdate;
}
public void updateDestination(String destinationUpdate){
this.destination = destinationUpdate;
}
public void updateWeight(int weightUpdate){
this.weight = weightUpdate;
}
}
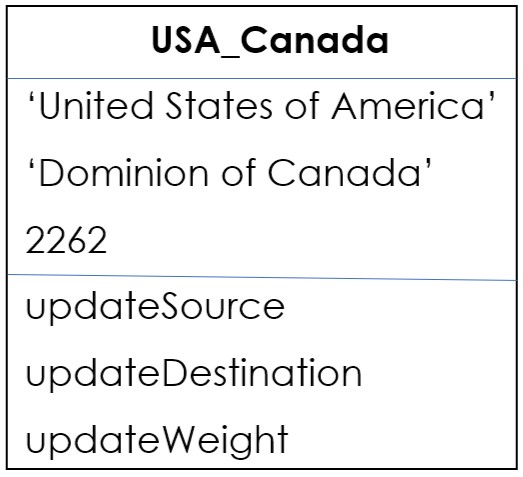
Structure of Edge:
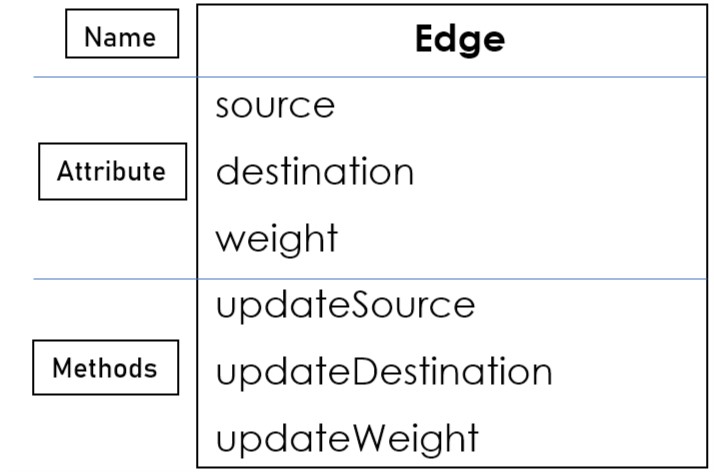
Let's create an object of the Edge.
// object initialisation
Edge USA_Canada = new Edge('USA','Canada',2300);
// update Source
USA_Canada.updateSource('United States of America');
// update Destination
USA_Canada.updateDestination('Dominion of Canada');
// update Weight
USA_Canada.updateWeight(2262)
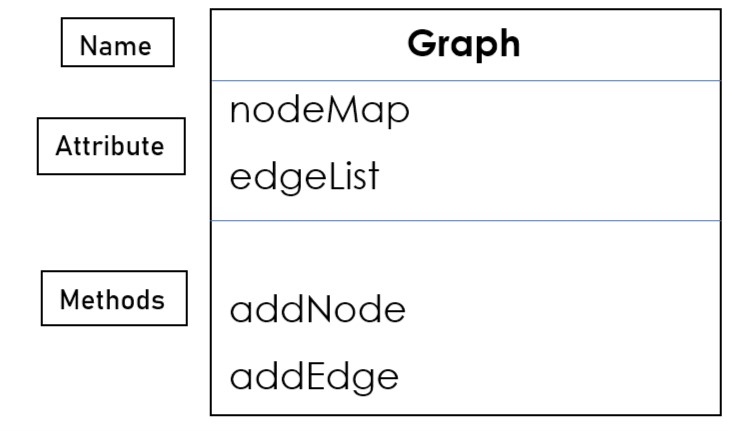
Now, Let's build a graph:
We are going to use two attributes(data structures) to build a graph.
-
nodeMap: Using a key-value pair i.e. map to store the graph where key is the identifier of the node and value is the reference to that node.
-
edgeList: Storing the objects of edges.
Methods Graph class should have:
-
addNode: Creating a new node of the graph and storing that into the map.
-
addEdge: Creating a new Edge of the graph and adding source into the neighbor list of destination and similarly destination into neighbor list of source.
So, here is the class of the graph:
class Graph{
Map<String,Node> nodeMap = new HashMap<String,Node>();
List<Edge> edgeList = new ArrayList<Edge>();
public addNode(String identifier){
nodeMap.put(identifier,new Node(identifier));
}
public addEdge(String source,String destination,int weight){
edgeList.add(new Edge(source,destination,weight));
nodeMap.get(source).addNeighbor(destination);
nodeMap.get(destination).addNeighbor(source);
}
}
Let's create an object of the graph:
// object initialisation
Graph graphObject = new Graph();
// adding Node
graphObject.addNode('USA');
graphObject.addNode('Canada');
// adding Edge
graphObject.addEdge('USA','Canada',2262);
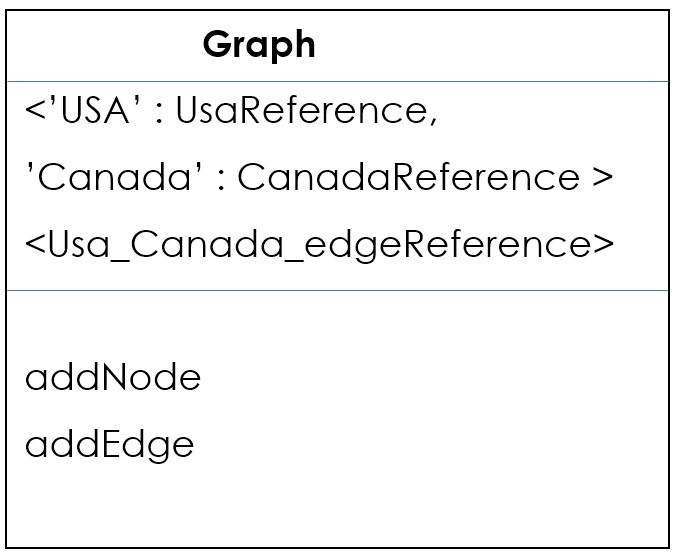
That's how we can build a graph.
Thanks for Reading.😀
